In a world the place land and water are working out, a quiet farming revolution is taking root — proper in folks’s backyards and terraces. Aquaponics is an modern farming method that integrates hydroponics and aquaculture, enabling the simultaneous cultivation of fish and vegetation utilizing minimal sources.
On this system, vegetation are grown in water whereas fish are raised in the identical or interconnected programs. The method is self-sustaining: the fish are fed, and their waste offers important vitamins for the vegetation, eliminating the necessity for chemical fertilisers.
This extremely natural strategy provides the additional benefit of twin earnings, as each fish and vegetation may be harvested.
This information provides tips about establishing a industrial aquaponics farm, overlaying essential features equivalent to setup processes, prices, fertilisation, pH and temperature administration, and water conservation.
1. How a lot area do you want?
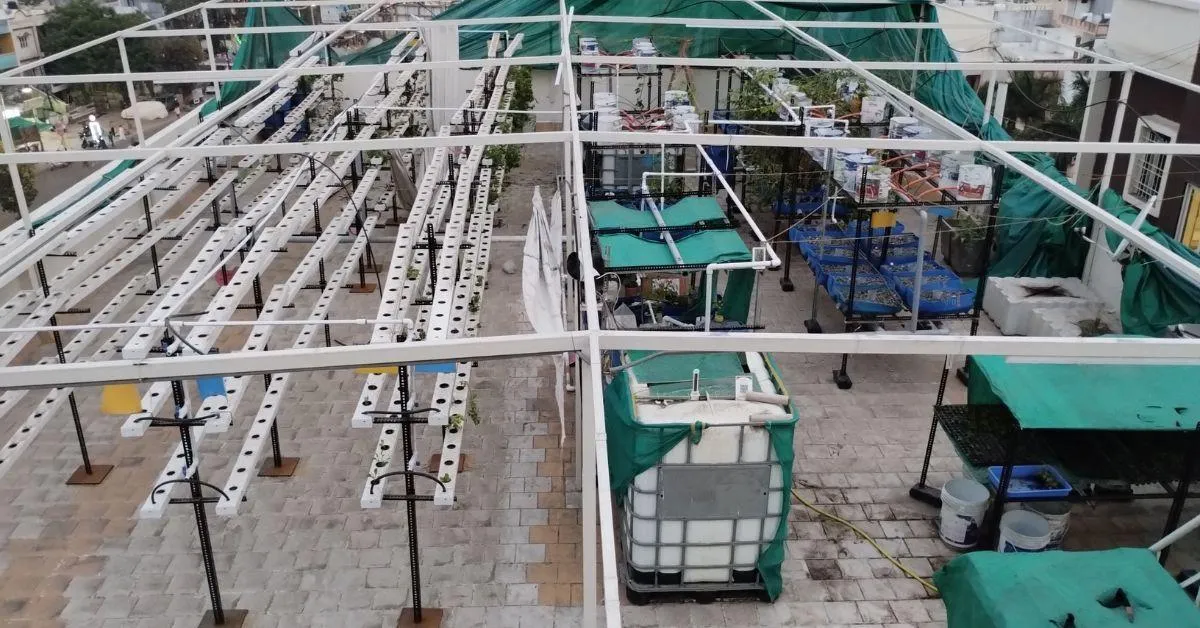
In line with Kerala-based farmer Vijayakumar Narayanan, an aquaponics farm may be arrange on lower than 900 sq ft of land. Ideally, half the area needs to be devoted to a fish pond and the opposite half to crops. This setup can assist as much as two tonnes of fish.
/english-betterindia/media/post_attachments/uploads/2025/06/aquaponics-1-1750920203.jpg)
2. What does the setup embody?
Incorporate parts equivalent to fish tanks, NFT pipes (Nutrient Movie Approach), water pumps, and bio-filters. Delhi-based Peter Singh, an aquaponics skilled who has constructed a inexperienced oasis to struggle air air pollution, recommends designing a system the place water from the fish tank circulates by means of plant beds, enriching it with vitamins from fish waste earlier than returning to the tank.
“This unit, measuring 2 ft by 6 ft and 6 ft in top, with synthetic lighting of 200 watts, makes use of 250 litres of water and might develop 180 vegetation. One can develop lettuce, kale, bok choy and different greens. One fish tank can maintain 5 kilograms of fish mass so that you could have 10 freshwater fish weighing half a kilogram every,” Singh explains.
3. Which fish must you begin with?
For inexperienced persons, farmers advise beginning with hardy species like Tilapia or decorative fish equivalent to goldfish and koi, which produce ample waste to nourish vegetation. You’ll be able to preserve round 150 fish in a 1,000-litre tank. For edible fish, a 3,000-litre tank is required to accommodate their development.
4. What’s the very best substrate for vegetation?
Vijayakumar suggests utilizing quartz silica sand for plant cultivation as it’s wealthy in natural content material and extra helpful than river sand. “Two pumps are wanted — one for blowing air into the pond and one other for pumping water to the sand biofilters the place the vegetation are grown. All these may be purchased beneath subsidies from the horticulture division,” he says. Vijaykumar earns as much as Rs 4 lakh per 12 months from this sort of farming.
/english-betterindia/media/post_attachments/uploads/2025/06/aquaponics-3-1750922166.jpg)
5. How a lot does it value to start?
Establishing a system on 150 sq ft requires an preliminary funding of round Rs 60,000 to Rs 65,000 for a set-up on 150 sq ft. Bengaluru-based Mamatha Kamireddy, who often conducts workshops on soilless farming strategies, suggests {that a} farm of this measurement can cater to the wants of a household of 5.
Establishing a terrace farm in a vertical configuration prices roughly Rs 800 per sq ft. Avoiding vertical farming can scale back the associated fee by half — to Rs 400 per sq ft. These bills sometimes cowl the fish tank, pumps, lighting, and preliminary inventory of fish and vegetation.
6. Do you want fertilisers?
Aquaponics primarily depends on fish waste, which comprises ammonia. That is transformed into nitrates by helpful micro organism, serving as an efficient fertiliser for vegetation.
Vadodara-based Shashank Dubey, an engineer who stop his company job to practise terrace aquaponics full-time, explains that in aquaponics, the fish excreta is decomposed by micro organism into nitrate, which is a perfect fertiliser for vegetation. “Via this fish tank, water is regulated all through small tanks that maintain vegetation.” Shashank has creatively upcycled drums and cans to be used as fish tanks.
Extra inputs like iron nails, lime, and eggshells can be utilized to provide further vitamins. “The largest benefit of this methodology is that together with rising meals with out soil in much less area, it’s also natural. Additionally, there isn’t any must fertilise the vegetation individually,” says Shashank.
7. Easy methods to handle pH and temperature?
Vijayakumar says that testing and sustaining the proper pH worth of water are essential earlier than introducing fish to the system. Optimum pH ranges assist be sure that each fish and vegetation thrive.
Leafy greens require temperatures between 25-30°C. Strawberries and different hilly crops develop finest at 18°C, whereas lettuce thrives at round 15°C. Use city clay pots for temperature regulation.
8. Does it actually save water?
Aquaponics programs recycle water, drastically decreasing consumption — by as much as 80 % in comparison with conventional farming. The system reuses water constantly, with losses occurring solely by means of evaporation.
Edited by Vidya Gowri