Within the Nineteen Nineties, should you had seen anybody pull out a digicam at a household gathering or weddings, chances are high you had a roll of Kodak movie inside it. This model was once part of individuals’s lives.
However right here comes the plot twist: Kodak is the corporate that taught the world methods to seize reminiscences, however couldn’t save its personal. By 2012, the enormous that when held 90% of the U.S. movie market filed for chapter.
In the meantime, Fujifilm, one other title from the movie period, was going through the identical state of affairs. There was no movie left sooner or later as a result of digital cameras had been destroying it. But, whereas Kodak crumbled, Fujifilm considered reinventing itself. Fujifilm reworked right into a multi-billion-dollar innovator from cosmetics to healthcare to superior cameras.
So why did one large collapse whereas the opposite rose stronger than ever? Let’s discover the fascinating story of Fujifilm’s survival and Kodak’s downfall, and what each enterprise immediately can be taught from it.
The Golden Age of Movie: Kodak’s Period of Dominance
The Penalties of the Digital Revolution: A “Crappy” and Vanishing Enterprise
How Fujifilm Overcame Disaster and Efficiently Reinvented?
The Golden Age of Movie: Kodak’s Period of Dominance
Lengthy earlier than the digital wave, each Kodak and Fujifilm thrived in a enterprise mannequin that appeared bulletproof. Whereas they made cameras, the true cash got here from movie and photograph improvement. Kodak perfected what it referred to as the “silver halide” technique: give away or promote cameras cheaply, then make huge earnings when individuals got here again for movie, chemical compounds, and paper. It was the identical playbook utilized by Gillette with razors and blades, or printer makers with printers and ink.
Fujifilm wasn’t far behind. In 1986, it introduced disposable cameras to the plenty, and Kodak adopted in 1988. By 2000, movie was nonetheless king, making up 72% of Kodak’s income and 66% of its working earnings, whereas Fujifilm relied on it for 60% and 66% respectively. What made movie such a fortress enterprise was its complexity. A single roll wasn’t simply plastic and chemical compounds; it was a masterpiece of engineering. Shade movie had 20+ ultra-thin layers, every one delicate to completely different colours of sunshine, constructed with microscopic precision.
As Kodak’s former VP Willy Shih put it, making shade movie was like “working 24 layers of superior chemical compounds at 300 toes per minute, all in whole darkness.” That complexity created excessive entry limitations. Dozens of corporations as soon as produced black-and-white movie, however when shade got here in, solely a handful survived. Ultimately, the market grew to become a two-horse race between Kodak and Fujifilm, with Agfa and Konica trailing behind. Regardless of fierce value wars, Fuji famously undercut Kodak within the 80s and 90s; the enterprise remained safe, worthwhile, and predictable for many years.
The Penalties of the Digital Revolution: A “Crappy” and Vanishing Enterprise
2001: The Peak Earlier than the Fall
- Movie gross sales reached their peak worldwide.
- However because the president of Fujifilm warned: “A peak all the time conceals a treacherous valley.”
- Gross sales began shrinking slowly, then quickly, finally dropping 20–30% per 12 months.
- By 2010, international demand for photographic movie had fallen to lower than one-tenth of what it was in 2000.
Shift from Movie to Digital
- The market didn’t disappear in a single day; it modified.
- With the rise of the web and private computer systems within the 90s, customers moved to digital cameras.
Drawback: Digital imaging relied on semiconductors, a platform utterly completely different from movie manufacturing.
The Draw back of Going Digital
- Not like movie, digital digicam expertise was modular; any engineer may assemble a digicam from elements.
- Entry limitations vanished; dozens of corporations entered the market.
- Kodak’s CEO, Antonio Perez, referred to as digital cameras a “crappy enterprise” as a result of: margins had been extraordinarily low and merchandise grew to become commodities as a substitute of premium items.
GoPro Instance – The Commoditization Impact
- A California surfer (GoPro founder) disrupted the video recorder market.
- However quickly, even GoPro was outcompeted by cheaper Chinese language producers.
- This highlighted how low entry limitations crushed profitability.
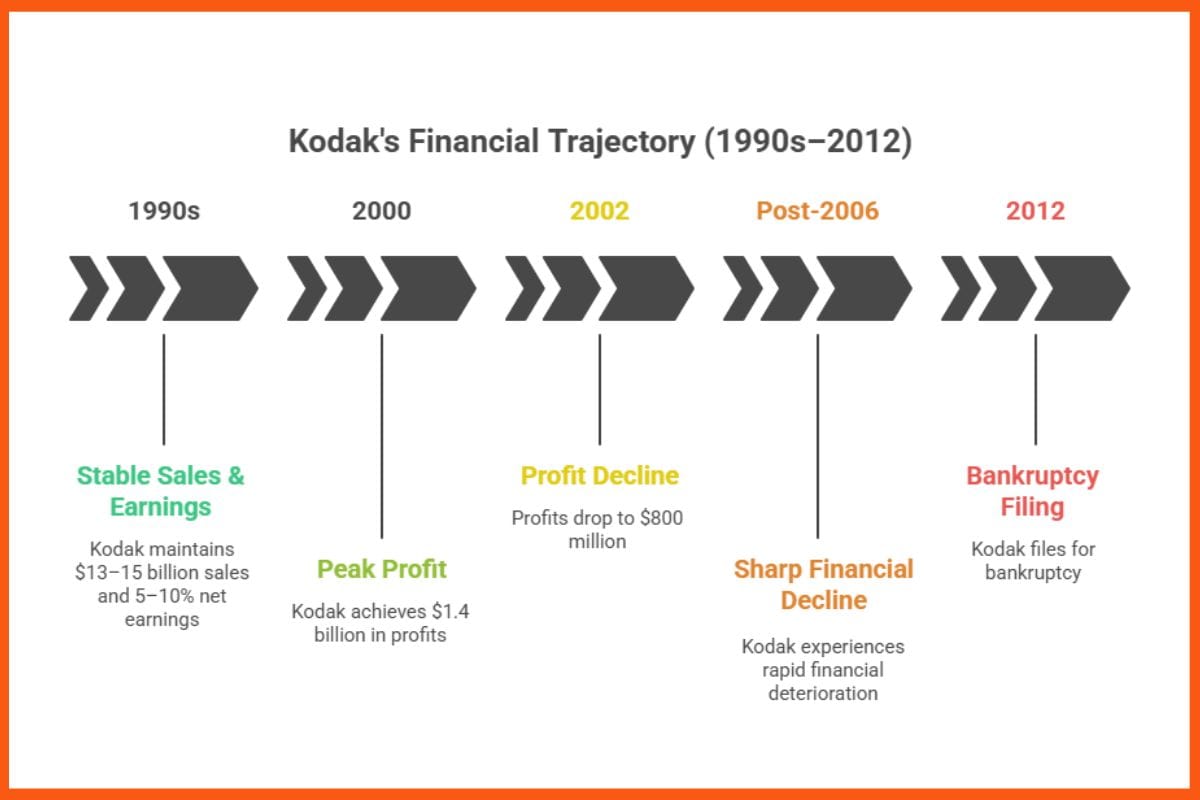
Kodak’s Monetary Struggles
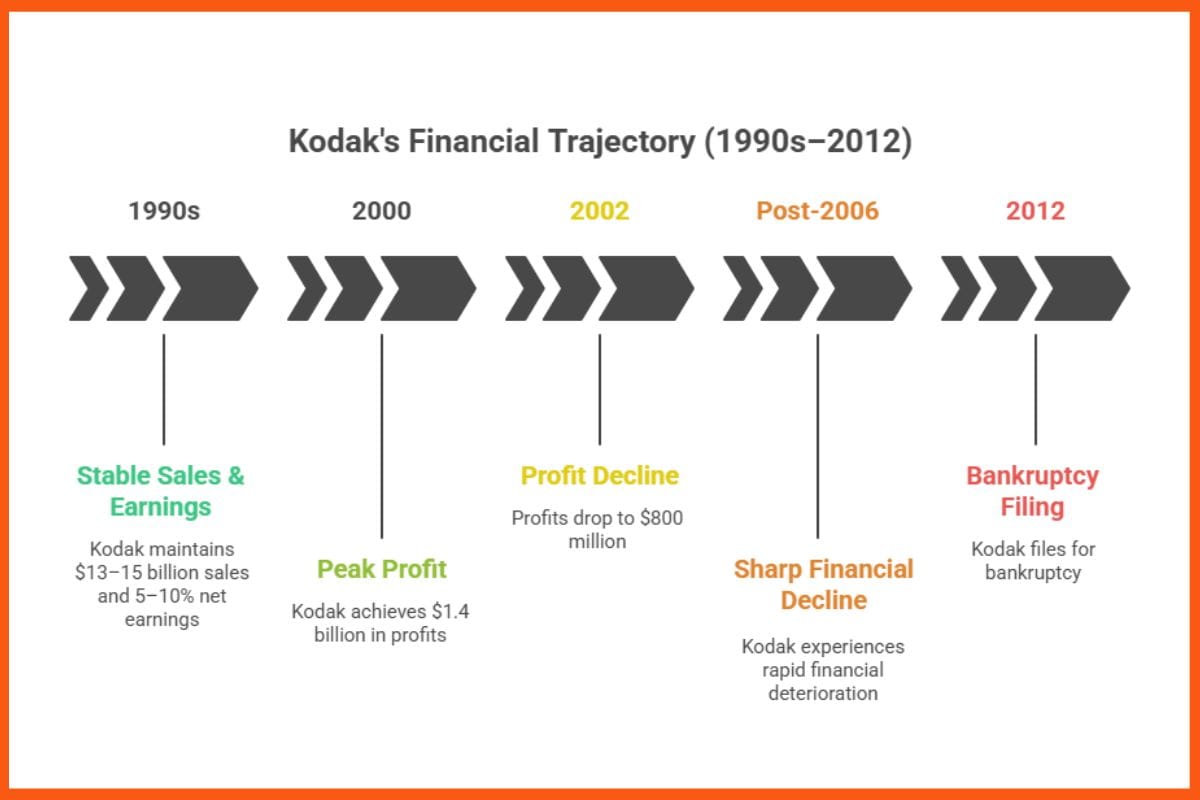
- Nineteen Nineties: Kodak gross sales hovered between $13–15 billion with strong 5–10% internet earnings.
- 2000: Income of $1.4 billion.
- 2002: Income fell to $800 million.
- Put up-2006: Sharp monetary decline resulting in chapter in 2012.
Kodak’s Digital Digital camera Paradox
Kodak offered plenty of digital cameras:
- 2005: Captured 21.3% of the U.S. market (ranked #1).
- Gross sales grew 15% that 12 months.
- However globally, it misplaced market share.
- 1999: 27% share → 2003: 15% → 2010: 7%.
The principle downside: They weren’t worthwhile.
- A Harvard research revealed Kodak misplaced $60 per digital digicam in 2001.
- In 2011, Kodak’s movie gross sales made $34M revenue, however digital cameras misplaced $349M.
Fujifilm Confronted the Identical Storm, however Survived
- The president admitted: “The photographic movie market had shrunk a lot quicker than we anticipated.”
- Between 2005 and 2010:
- Shade movie gross sales fell from ¥156 billion → ¥33 billion.
- Photograph ending dropped from ¥89 billion → ¥33 billion.
- Not like Kodak, Fujifilm not solely survived however sustained itself by reinventing itself.
Causes Why Kodak Failed | Kodak Failure Case Examine
Why did Kodak fail after over a century of dominance within the area of pictures & videography? Learn this case research on Kodak’s failure & chapter.

How Fujifilm Overcame Disaster and Efficiently Reinvented?

When the movie market collapsed (falling to lower than 10% of its 2000 measurement by 2010), Fujifilm was in serious trouble. Movie as soon as made up 60% of its gross sales, however sticking to it will have meant sure loss of life, similar to Kodak. As an alternative, Fujifilm managed to develop income by 57% over the subsequent decade, whereas Kodak’s gross sales fell by 48%.
Daring Management and Imaginative and prescient 75
- In 2000, Shigetaka Komori grew to become president of Fujifilm.
- By 2004, he launched a six-year plan referred to as VISION 75 (named after Fujifilm’s seventy fifth anniversary).
- The mission was clear: “Save Fujifilm from catastrophe and guarantee its viability as a number one firm with gross sales of two–3 trillion yen a 12 months.”
Restructuring and Innovation Push
- Downsized the movie enterprise by closing redundant amenities.
- Merged analysis divisions into one centralized R&D hub to drive innovation and collaboration.
- Accepted that digital cameras couldn’t change movie earnings and appeared for brand new development engines.
Know-how Audit and Market Mapping
- Komori ordered R&D to stock Fujifilm’s applied sciences and examine them with international market wants.
- After 18 months, engineers recognized areas the place current experience may gasoline new companies:
- Prescription drugs
- Cosmetics
- Extremely useful supplies
Profitable Bets on Rising Markets
- LCD Screens: Tailored a photograph movie expertise to create FUJITAC, a high-performance movie important for LCD panels. At present, FUJITAC controls 70% of the worldwide marketplace for protecting LCD polarizer movies.
- Cosmetics: Constructed on its experience in gelatin and collagen (key for each photograph movie and human pores and skin). In 2007, Astalift, a skincare and cosmetics model, grew to become profitable in Asia.
Development By means of Acquisitions
- Used M&A to hurry up entry into new industries. Key strikes included:
- Toyama Chemical (2008): Entry into prescribed drugs.
- Fujifilm RI Pharma: Strengthening radiopharmaceuticals.
- Fuji Xerox (2001): Turned a consolidated subsidiary after rising stake by 25%.
Transformation by 2010
- 60% of income and two-thirds of revenue got here from movie in 2000.
- Imaging made up lower than 16% of income by 2010.
- Fujifilm had develop into a diversified expertise powerhouse spanning healthcare, cosmetics, imaging, and superior supplies.
Conclusion
Fujifilm and Kodak’s story teaches us a precious lesson about dealing with change. Kodak failed as a result of it didn’t change from what it had all the time performed. However, Fujifilm accepted the change. The corporate began new varieties of companies utilizing its data.
In immediately’s world, Fujifilm is a number one firm in healthcare, skincare, electronics, and plenty of different fields. With Kodak, which was once an enormous title in cameras, others must be cautious about not innovating. Fujifilm succeeded as a result of it was prepared to attempt new issues and never simply depend on its previous enterprise. It is very important have the ability to change and plan for the long run based mostly on the story.
Nikon’s Advertising and marketing Methods: Specializing in the Future
Nikon’s success stems from its superior expertise, efficiency, and high quality, in addition to its efficient advertising and marketing methods resembling robust branding, buyer engagement, and distinctive service.

FAQs
Why did Kodak fail whereas Fujifilm survived?
Kodak failed as a result of it resisted change and stayed depending on movie, whereas Fujifilm embraced diversification into cosmetics, healthcare, and electronics, making certain survival past pictures.
What was Fujifilm’s Imaginative and prescient 75 technique?
Launched in 2004 by Fujifilm president Shigetaka Komori, Imaginative and prescient 75 was a six-year transformation plan that restructured operations, drove innovation, and diversified the corporate into new industries like healthcare and electronics.
Did Kodak invent digital cameras?
Sure, Kodak developed the primary digital digicam prototype in 1975 however didn’t commercialize it successfully, fearing it will cannibalize its worthwhile movie enterprise.
WIDGET: questionnaire | CAMPAIGN: Easy Questionnaire